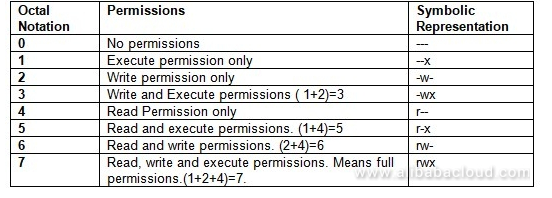
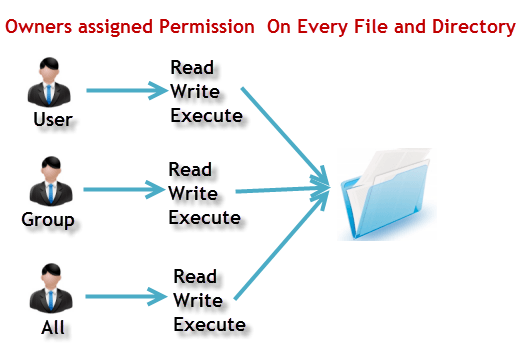
Chmod Octal Table
For example, to set permissions on a file to rwxrwxr–, you would run:.

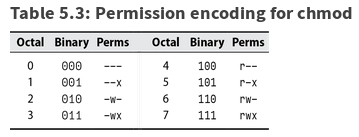
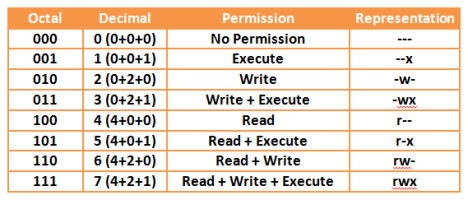
Chmod octal table. The permission in octal form is useful for many commands such as chmod command and other sysadmin tasks. The following table lists the summary of permissions denoted by octal values. The following table shows how the setgid and setuid file modes are represented in octal:.
// this is incorrect. Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which. This quick tutorial shows how to use the stat command to view octal file permissions.
Others and each view the full answer. An essential program that benefits from using octal notation is the chmod command. For example, give the user read/write/execute (octal 7 = rwx), group read/execute (octal 5 = r-x), and other read only (octal 4 = r--) for the file myfile:.
Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. Will add execute rights for Owner and Group, but will not modify other existing permissions on the file;. Since these bits are usually manipulated in groups of three, octal notation is commonly used when referring to them.
The umask command allows the mask to be set as octal (e.g. The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and stickyflags. Following table lists the octal values which can be used with chmod command.
The dir works in mo, inmediately remove the directory you see Capture transcript of memory REPLY IN WORKSEET Table of OK and Pochod Command line che Deep chmod 100 sep 3 chmod 0 top 4 8 CSOP chmod tep chmod 101 TENDO REPLY IN WORKSEETI you see any other or such as he wchle or directory you are not in the come directory when you are in the. And there you have it:. The syntax requires three octal digits, each representing the owner, group, and other permissions, respectively.
I am assuming you don't want the binary codes, though I quite like them, so here are the text codes:. You can also set permissions using the Numeric Mode. It can be invoked with either octal values representing the permission flags, or with symbolic representations of the flags.
So, the following work the same. The bits in the mask may be changed by invoking the umask command. The chmodnumerical format accepts up to four octal digits.
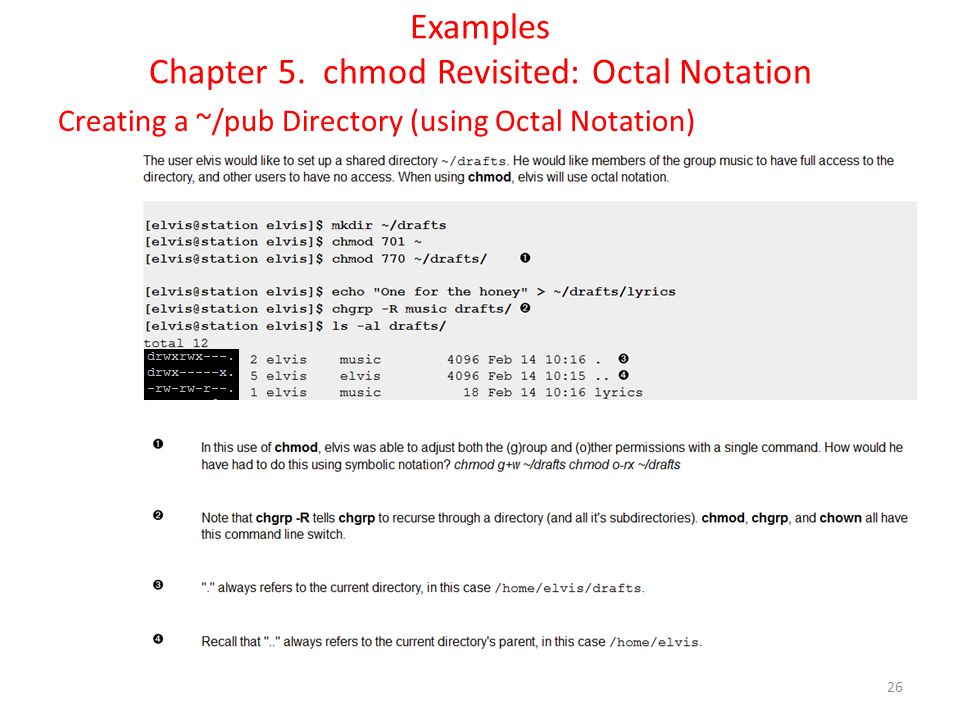
It can be applied recursively using the "-R" option. When we use the chmod command later on, you’ll see that you can change the permissions using either symbols or octal numbers. For example, let’s say you want to set the permissions for file.txt as rwxr–r–.
You can either use symbolic representation of changes or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. I propose here an easy manner to "build" this number. With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions.
Octal Number Representation So that’s how permissions are displayed in Linux using symbols. The following example sets read, write and execute permissions for user, group and world. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
While ASCII is limited to 128 characters, Unicode has a much wider array of characters and has begun to supplant ASCII rapidly. Give the user read/write/execute (octal 7 = rwx), group read/execute (octal 5 = r-x), and other read only (octal 4 = r--) for the file myfile:. This is a combination of three numbers by which we can represent all combinations of access rights.
Chmod 754 myfile Setgid and setuid. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. $ chmod 754 myfile.
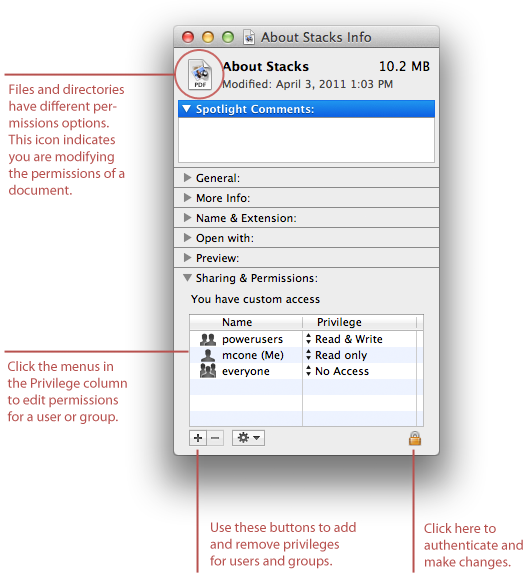
Select the permissions you require below. You can also set the exact permissions using symbolic modes. Remember, there is 4 digits, which correspond to something like "0, user, group, public":.
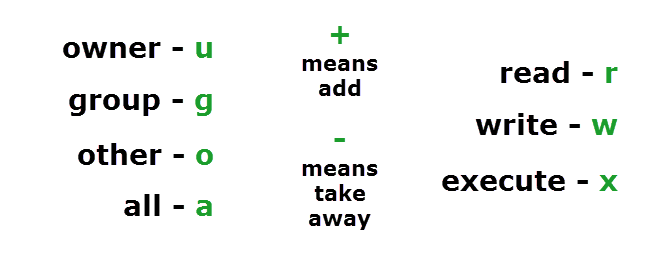
Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories. U = user g = group o = other (not user or group) a = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit. The octal notation would be calculated as follows:.
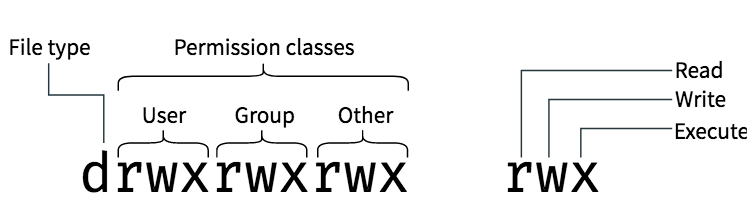
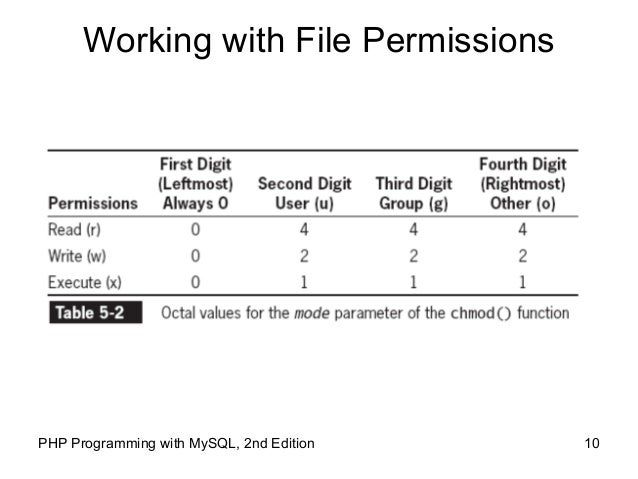
Using the octal notations table instead of ‘r’, ‘w’ and ‘x’. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. 0754) or symbolic (e.g.
The chmod command can be used with either a text-based argument or 3 octal digits (see note 1) to change the permissions on a file.An example of the text-based command to add "read" permission for group members and others to a file named foo is:. Chomd is one of the most powerful and important command in Linux. All of them are listed in man chmod, but I will type them out here as well.
$ chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r myfile. The chmod -R option allows you to recursively descend through directory arguments, setting the mode for each file as specified. The following table shows the equivalent octal and symbolic notations:.
See the “chmod” subsection in this chapter for details about octal notation. To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below. The following table shows how the setgid and setuid file modes are represented in octal:.
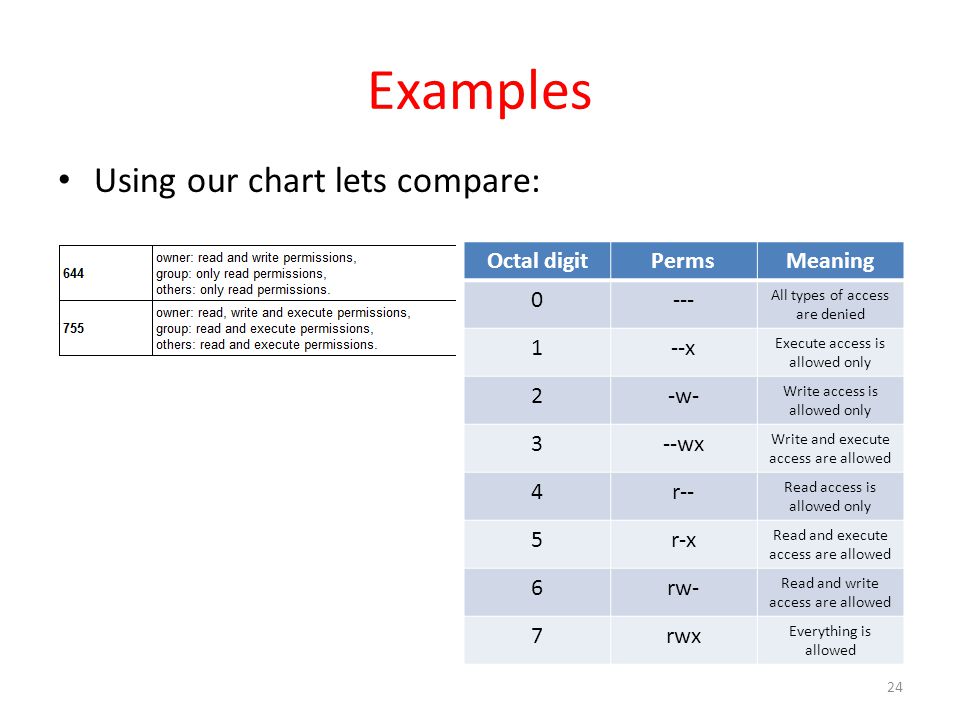
There are no relative assignments of permissions using octal. Example of octal modes:. For example, the value 644 sets read/write permissions for owner, and read-only permissions for group and other.
You can also use octal notations like this. U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Read w = write x = execute - = no. File Permissions File Permissions Table of contents.
Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. Chmod 640 file1 = rw- r-- ---chmod 754 file1 = rwx r-x r--chmod 664 file1 = rw- rw- r--Here’s an example command using octal numbers:. Unix or any *nix uses octal for permissions – it’s pretty simple once you get the chart into your brain 😉.
Basic Permissions Letter Format Octal Format Special permissions File Permissions Commands chown chgrp chmod Exercises Managing Software Managing Software Overview Packages Processes Services Exercises. The format of a symbolic mode is:. The values of the bits in these masks correspond to those used by the UNIX chmod(2) system call and chmod(1) user command, and are given in the following table.
Here are a few more examples of chmod statements in this form:. As such, all we need to do is enter the following command to change the file permissions. See the “chmod” subsection in this chapter for details about the chmod command.
We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. The table below gives numbers for all permission types of a File/Directory.
This CHMOD command is mainly used to set, edit and remove the file permission to the user, user group and others.This CHMOD can be expanded as “Change Mode“, the name itself it explains that it is mainly used to change the permission mode of a file.You can use this command to restrict the file by. Ugoa +-= perms. Chmod 754 myfile Setgid and setuid.
For example, give the user read/write/execute (octal 7 = rwx), group read/execute (octal 5 = r-x), and other read only (octal 4 = r--) for the file myfile:. Chmod u+s filename This works fine. Chmod 754 myfile Setgid and setuid.
These default permissions are applied only when the file or directory is initially created. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. The chmod command can also explicitly set permissions using a numerical representation.
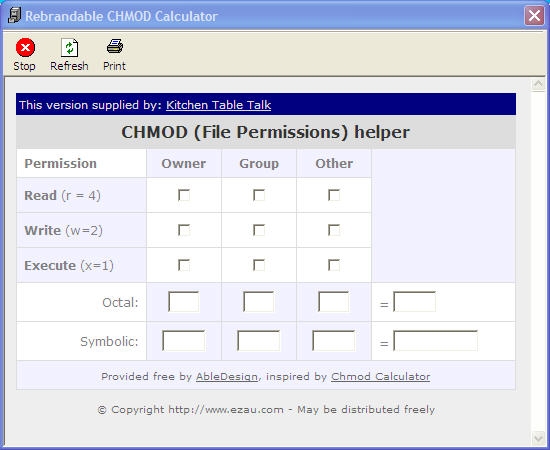
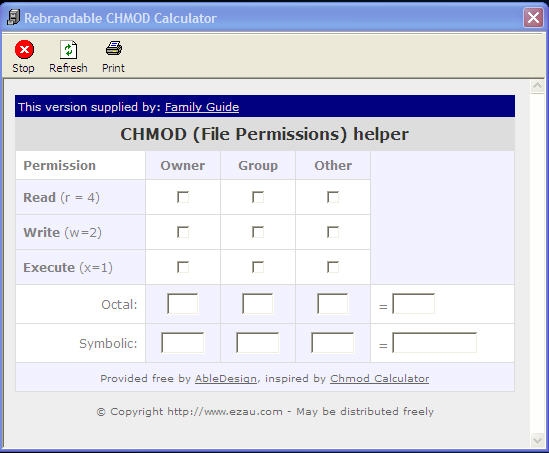
Using octal syntax for chmod allows setting the absolute permissions for owner, group, and other in one quick command. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. Similar to alphabetic notation, octal notation can include an optional leading character specifying the file type.
Instead of “u=rwx,go=rx”, you would have “755”. So if you take the octal digit that expresses the permissions in each category, and you line them up in order, you get a three-digit octal number. You use these numbers in sets of three to set permissions for owner, group, and other (in that order).
The second way to represent the same permissions is by using octal numbers. Chmod special modes Setuid and setgid. I understand (to some good extent) file permissions, the concept of umask, setuid and using octal numbers with chmod.
But the octal number 4000 is always associated with setuid (in books etc). A widely used, often shorter, form of calling chmod is by use of the octal notation. If the mask has a bit set to "1", it means the corresponding initial file permission will be disabled.A bit set to "0" in the mask means that the corresponding.
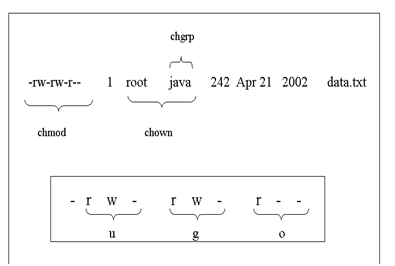
Chmod changes the file mode of each specified FILE according to MODE, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. This is followed by owner permissions, group owner permissions, and other permissions respectively. >>>>> before going through answers you shoud know about permissions 1.
For example, this command also sets 754 permissions:. How to set permissions with chmod in octal mode. When symbolic links are encountered, their mode is not changed and they are not traversed.
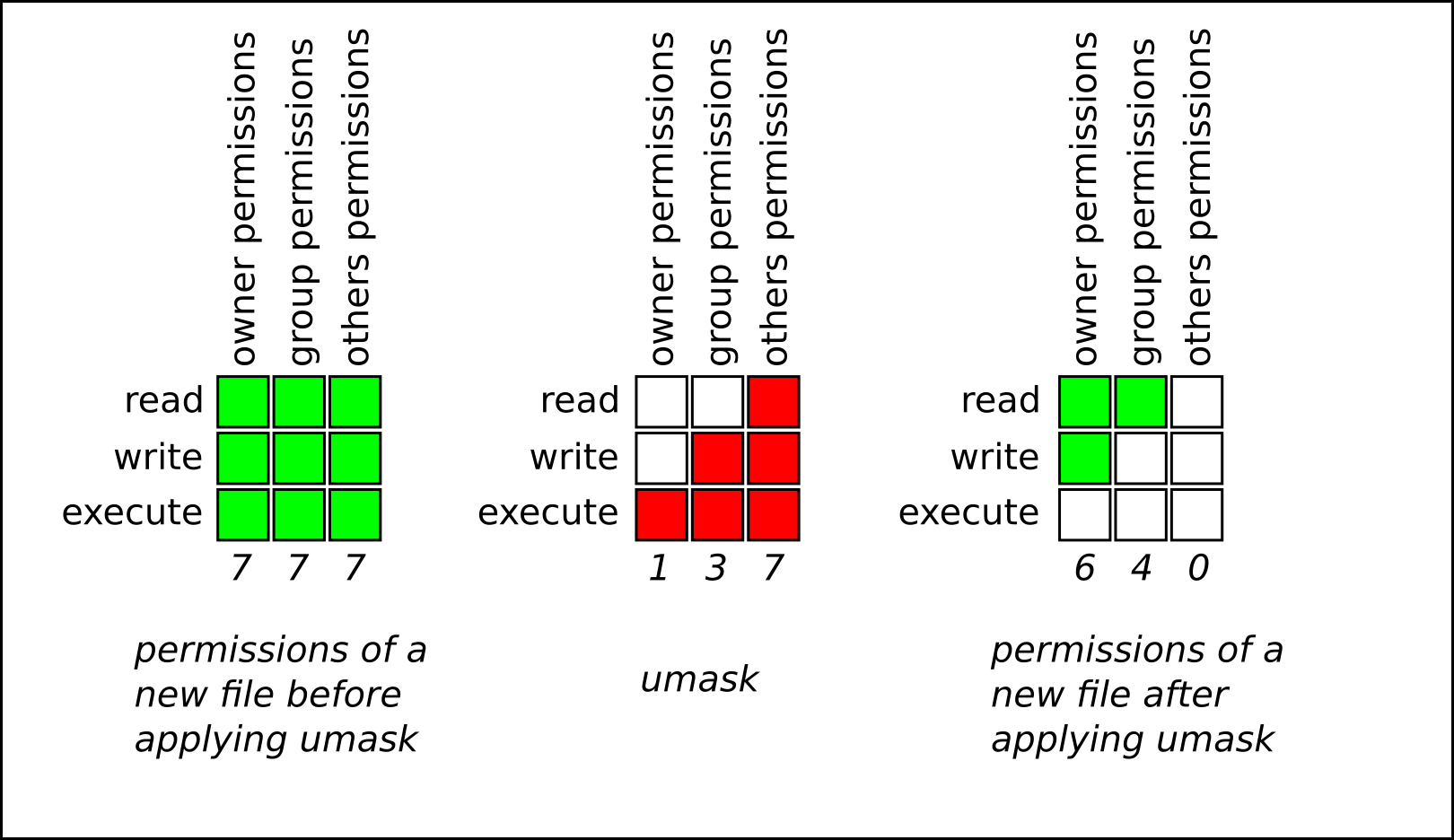
The following table shows how the setgid and setuid file modes are represented in octal:. The following table shows how the setgid and setuid file modes are represented in octal:. Umask or file mode creation mask is a grouping of bits, each of which restricts how its corresponding permission is set for newly created files or directories.
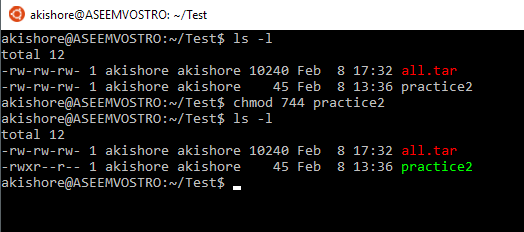
In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. By referring to the above table, you can see that the numeric representation of this permission is 744. The octal values have the following meaning:.
Chmod is a GNU utility which is provided as part of coreutils rpm in Linux distributions chmod is short abbreviation for " Change Mode " It is used to change the file mode bits of each given file/directory according to mode. Using octal values to change access You can also use numbers (octal values) instead of letters to set the permissions. It may be represented as binary, octal or symbolic notation.
Binary executables with the setgid bit (chmod g+s path) can be executed with the privileges of the file's group. How to get octal file permissions on Linux/Unix command line. HMOD Command in Linux:.
Setuid and setgid (short for 'set user ID upon execution' and 'set group ID upon execution', respectively) are Unix access rights flags that allow users to run an executable with the permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories. The octal values assigned to the permission modes are (they also have letters associated with them that are displayed by programs such as ls and can be used by chmod):. PERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w = writable x = executable - = no permission.
Three parties involved a. Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu. Using the Chmod Command.
The mask is stored as a group of bits. /home/user> ls -l foo-rwx--x--- 1 user user 78 Aug 14 13:08 foo /home/user> chmod go+r foo /home/user> ls -l foo-rwxr-xr-- 1. But I still cannot figure out the relationship between the octal number 4000 and setuid.
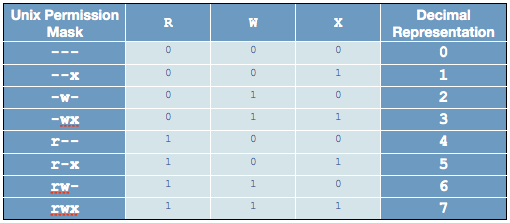
Rwx = 4+2+1 = 7 r-x = 4+2+0 = 6 r-- = 4+2+0 = 6 Ultimately, this would give us 766 as the corresponding octal notation to rwx-rw-rw-. Chmod ugo+rwx file_name chmod 777 file_name. The umask command sets default permissions for files and directories.
Checking the effect of running chmod -R ugo=rwx /local/project-a chmod -R 777 /local/project-a — The result is the same. Each digit octal notiation can be used of either of the group ‘u’,’g’,’o’. $ chmod 774 file_name.
$ chmod 744. In php, you have to use chmod with octal values, you cannot write something like :. In octal, the setgid bit is represented by 00e.g:.
U - user g - group o. Chmod¶ The chmod ("change mode") command is used to change the permission flags on existing files. Chmod 754 myfile Setgid and setuid.
For example, give the user read/write/execute (octal 7 = rwx), group read/execute (octal 5 = r-x), and other read only (octal 4 = r--) for the file myfile:. A useful property is to set the setgid bit on a directory so that all files and directories newly created within it inherit the group from that directory. This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options.
The Linux chmod command also supports octal notation. The umask command is used with Unix-like operating systems, and the umask function is defined in the POSIX.1 specification.
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Standard Linux Text Book
Chapter 5 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal
Chmod Octal Table のギャラリー

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders
Ppt Contents Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Tinyapps Org Palm Os
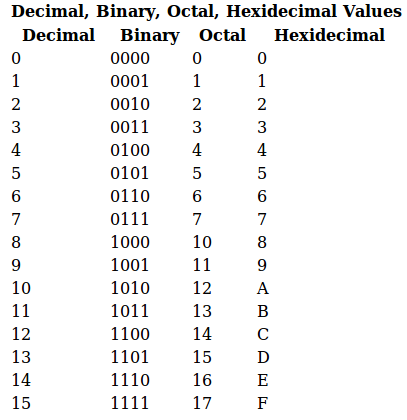
Binary To Octal

Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Read Write Access Chmod 775

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Linux File Permissions Train With Ctg

Sharing Files On Linux Security Setting Coding Tools And Resources

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

File Permission In Linux Chmod Command Armantutorial
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

Explain Unix File Permissions
Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference

14 Permission And Modification Times

Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev
Q Tbn 3aand9gctejwme2dmdomohoy140oy72qp3e1pn8jtuanchtus Usqp Cau

Standard Linux Text Book
Kitchen Table Talk Chmod Calculator Standaloneinstaller Com
Ict Innovation Lpi 104 5 Wikieducator

Linux Command For Beginners
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
Family Chmod Calculator Standaloneinstaller Com
Cs 480 Lec 8 Spring 19

Octal Table 2yamaha Com

Unix Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Changing Permissions In Linux System Dev

Standard Linux Text Book

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics Data Online Safety Privacy

Linux File Permission Management Summary Programmer Sought

Linux Unix Changing Permissions With Chmod Vinish Kapoor S Blog
Contents

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Introduction To Unix Family File Permissions Learning Tree Blog

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Octal Table 2yamaha Com

Files Directories Objectives To Be Able To Describe And Use The Unix File System Model And Concepts Contents Directory Structure File System Concepts Ppt Download

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Chmod Encoding Table Chmod Encoding Table Tek Bahadur Limbu Flickr

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsacd7mr Ecztzl Lq8wap9enfi2vj2xlffbqx6amvc25tn3 R6 Usqp Cau

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange
2

Unix Chmod Cheat Sheet

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

File Security

Can We Set File Permissions To 775 By Using Umask In Linux If Yes What Would The Umask Be And How Will It Be Calculated Quora

Chmod Group Write Access
Solved 3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Permi Chegg Com

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod This Part Of The Lab Needs To Be Executed As Chegg Com
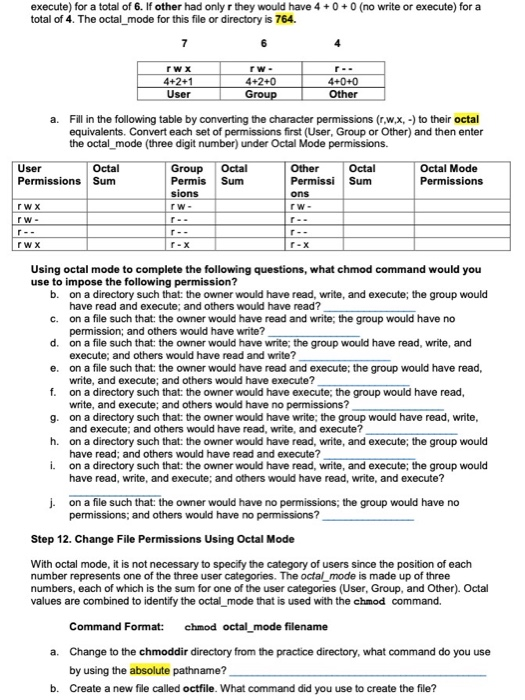
Class File Tree Structure Home Csc156 Yourusername Chegg Com

How To Change Existing Permission Numerically
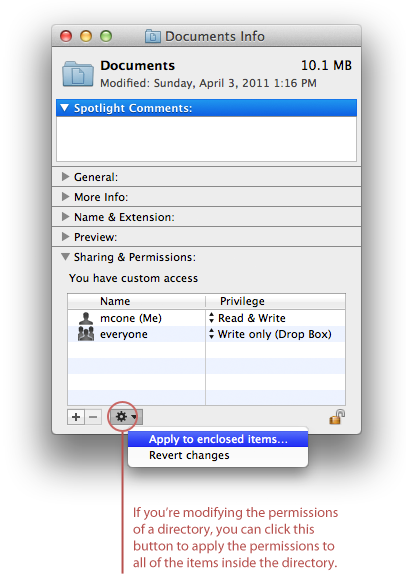
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
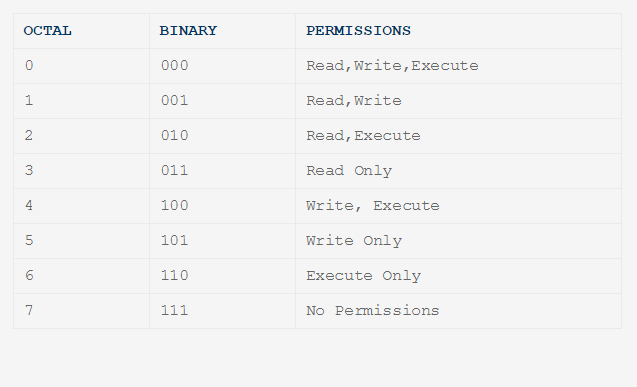
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Thelinuxcommandline Part 1 Learning The Shell Flashcards Quizlet

Chmod Wikipedia
Sharing Data Cc Doc
Learn Oracle Database Administration Unix Permissions Table
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod 664

Linux Users And Groups Linode
2

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Linux Commands Frequently Used By Linux Sysadmins Part 4
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Understanding File Permissions In Unix Or Linux And Modify Using Chmod

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Octal Table 2yamaha Com
A Quick Introduction To Unix Permissions Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
New Bash Linux Cheat Sheet Wallpaper Download Free 40 X 3050px

19b Permissions
Linux Chmod Tips

Os Mkdir And Os Mkdirall Permission Value

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex
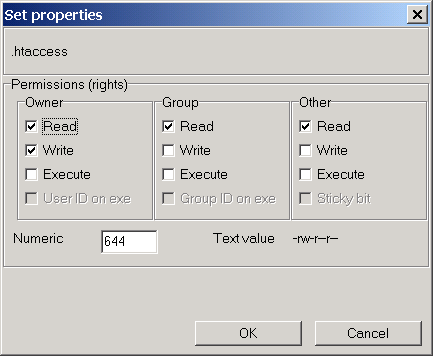
Chmod Help

Please Help Me Out With This All I Will Surely Gi Chegg Com

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Http Teaching Idallen Com Cst07 13w Notes Worksheet08 Pdf
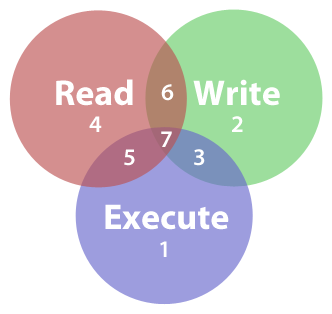
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
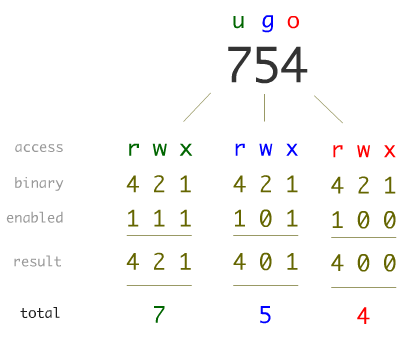
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqzjwejtv9wexgnjg6wrv4scdirjlf8ko Drmhmencfjup H30u Usqp Cau

Foundation Topics Exploiting Local Host Vulnerabilities Exploiting Local Host And Physical Security Vulnerabilities Pearson It Certification

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Solved 3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Permi Chegg Com



